Blood Sugar Monitoring for Diabetics
Table of Contents
Introduction
A vital component of managing diabetes is blood sugar monitoring, which enables diabetics to keep tabs on their blood sugar levels and make educated decisions regarding their course of care and way of life. We will discuss many facets of the significance, advantages, and real-world applications of blood sugar monitoring for diabetics in this comprehensive explanation.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
The body’s cells and organs use blood sugar, commonly referred to as blood glucose, as their primary source of energy. However, blood sugar regulation is compromised in diabetics, resulting in either hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Diabetes patients can avoid consequences from poorly managed diabetes and maintain optimal glucose control by keeping a close eye on their blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Blood Sugar Monitoring
1. Optimizing Treatment Plans: Frequent blood sugar monitoring gives medical professionals important information that they can use to customize treatment regimens for each patient. Healthcare providers can accomplish optimal blood sugar control by monitoring glucose levels throughout the day and adjusting medication dosages, dietary suggestions, and exercise regimens.
2. Preventing Complications: Blood sugar levels that are consistently high can raise the chance of developing long-term issues like heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, nerve damage, and visual issues. By enabling diabetics to quickly detect and manage changes in blood sugar levels, blood sugar monitoring lowers the risk of complications and enhances overall health outcomes.
3. Managing Hypoglycemia: Excessive insulin or oral medication, missing or postponing meals, or increasing physical activity can all lead to low blood sugar levels. Diabetes patients can identify hypoglycemia early and take corrective measures, including eating fast-acting carbs, to bring their blood sugar levels back within a safe range by keeping an eye on their blood sugar levels.
4. Adjusting Lifestyle Choices: Blood sugar monitoring empowers individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices. By tracking the impact of diet, exercise, stress, and other factors on their glucose levels, diabetics can identify patterns and make adjustments to their daily routines to better manage their condition.
Methods of Blood Sugar Monitoring
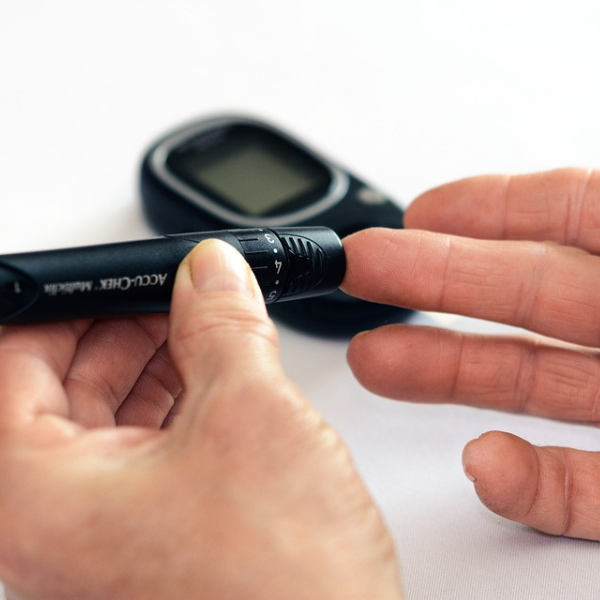
1. Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): SMBG involves using a glucometer to measure blood sugar levels using a small drop of blood obtained by pricking the finger with a lancet. This method allows diabetics to check their glucose levels at home or on the go, providing immediate feedback on their current blood sugar status.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): A tiny sensor that is implanted beneath the skin is used by CGM devices to continuously check glucose levels day and night. By offering trend data and real-time glucose measurements, these gadgets help diabetics monitor changes in their blood sugar levels over time.
3. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Testing: The percentage of hemoglobin that is glycated (bound to glucose) is measured by the HbA1c test, which determines the average blood sugar levels during the previous two to three months. This test aids healthcare professionals in assessing the efficacy of diabetes management techniques by giving a comprehensive picture of long-term glucose regulation.
4. Frequency of Monitoring: Blood sugar monitoring frequency varies based on individual circumstances, including diabetes type, treatment plan, lifestyle, and general health. While some people may need to check their blood sugar levels several times a day, others might just need to check them occasionally.
5. Timing of Monitoring: When fasting (before meals), postprandial (after meals), before and after exercise, and before bedtime, diabetics should pay close attention to their blood sugar levels. Observing at different times offers important information about the ways in which different circumstances influence blood sugar levels.
6. Recording and Interpretation: Diabetics and healthcare professionals can see patterns and trends in glucose control by keeping a diary of blood sugar measurements and associated variables like meals, medications, physical activity, and symptoms. Diabetics are better equipped to make decisions regarding their diabetes care when they are aware of the relevance of blood sugar levels and trends.
7. Communication with Healthcare Team: Regular communication with healthcare providers, including physicians, diabetes educators, and registered dietitians, is essential for effective blood sugar management. Discussing blood sugar monitoring results, treatment goals, and concerns allows diabetics to receive personalized guidance and support to optimize their diabetes care.
Lastly, blood sugar monitoring is essential to managing diabetes since it offers important information on glucose regulation, the efficacy of treatment, and general health. People with diabetes can improve their treatment plans, avoid complications, and have better long-term results by closely collaborating with their healthcare team and routinely checking their blood sugar levels. With the right information and understanding, diabetics can manage their illness and lead longer, happier lives.




5 thoughts on “Why is Blood Sugar Monitoring Important for Diabetics?”